logging¶
Use standard module logging to print logs. It defines five levels of logs: DEBUG < INFO < WARNING < ERROR < CRITICAL and contains four basic classes: Logger, Handler, Filter and Formatter.
Get Started¶
Print simple logs by calling module-level functions. Following calls will print logs onto the console.
import logging
logging.debug('This is a debug log.')
logging.info('This is a info log.')
logging.warning('This is a warning log.')
logging.error('This is a error log.')
logging.critical('This is a critical log.')
logging.log(logging.DEBUG, 'This is a debug log.')
By default, only WARNING or above logs will be printed onto console. To modify basic configurations, we need to call logging.basicConfig() with following optional arguments.
- filename specifies target file that logs are output to.
- filemode specifies mode to open target file, 'a' by default.
- format specifies format to output logs. Refer to LogRecord attributes.
- datefmt specifies format of date/time, taking effect when format contains time field. Refer to time.strftime().
- level
- stream specifies stream logs are output to, such as sys.stdout and sys.stderr.
- style specifies style of format string. Optional values includes '%'(default), '{' and '$'. It's since Python 3.2.
- handlers specifies handlers to handle logs. It's since Python 3.3.
filename, stream and handlers are incompatible. If both are present, a ValueError is raised.
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='example.log', level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s | %(levelname)s | % (message)s', datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %I:%M:%S')
logging.info('Hi, %s', 'Jack')
It will print the following log.
Advanced¶
Create an instance of Logger to record logs by calling logging.getLogger('name'). Its procedure shows as follows.
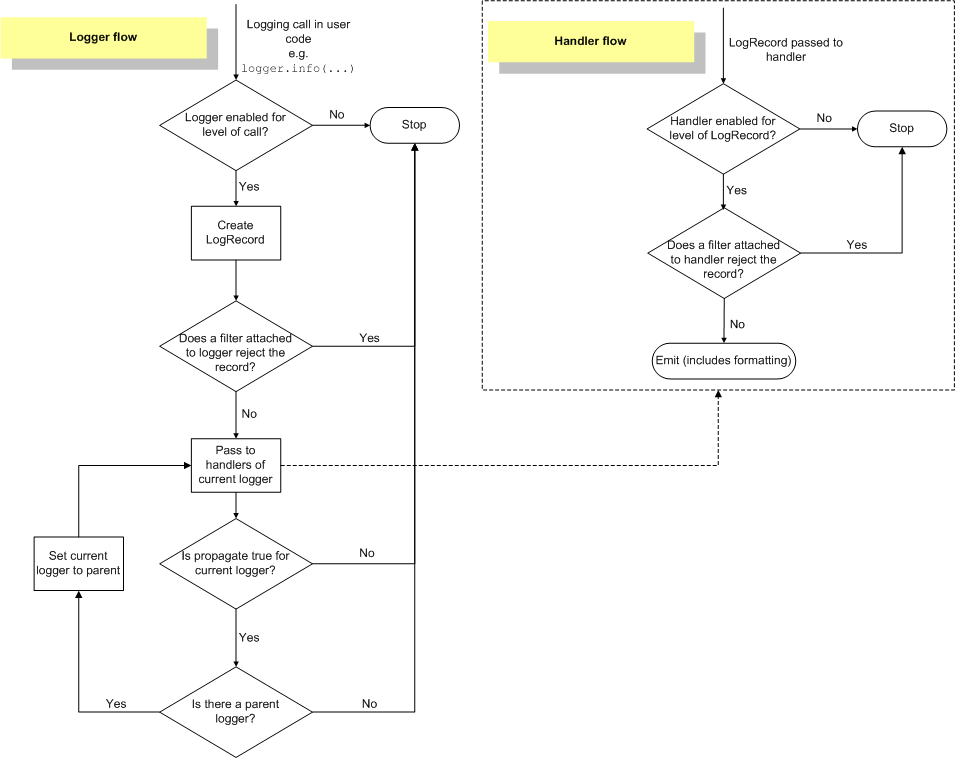
Loggers¶
The most common used methods of Logger fall into two categories:
- configuration
Logger.setLevel()Logger.addHandler()andLogger.removeHandler()Logger.addFilter()andLogger.removeFilter()
- message sending
Logger.debug(),Logger.info(),Logger.warning(),Logger.error()andLogger.critical()Logger.exception()Logger.log()
Handlers¶
Formatters¶
Configuration¶
There are three ways to configure logging:
- Creating loggers, handlers, and formatters explicitly using Python code.
- Creating a logging configuration file and reading it using the
fileConfig()function. - Creating a dictionary of configuration information and passing it to the
dictConfig()function.